Table of Contents
Video conferencing apps have become the new normal in modern workplaces. These tools serve as indispensable components for modern businesses allowing them to achieve maximum efficiency while practicing remote and hybrid working models. Video conferencing apps provide companies the possibility to overcome challenges fostering efficient communication and bringing the team closer together.
Zoom, Cisco WebEx, Teams by Microsoft, Meets by Google and Slack are the ones of the most popular options for video conferencing on the web and we were approached to develop its competitor.
Fortunately, there are many technologies and ready-made components which enable us to build a video conferencing application fairly quickly.
In this article, we will have a look at the development of a video conferencing application based on WebRTC.
First section introduces the client’s requirements, which include common features, but also some less-common ones, for example streaming the video conferencing to the RTMP server or bridging WebRTC with Cisco SIP devices. We describe technological challenges in the next section including hardware and network requirements, software compatibility challenges, interfacing, end-to-end encryption and virtualization.
Next, we describe our solution composed of existing technologies, customized and built from scratch, and for that, it is best to choose a reliable software house, for example Altamira.
Client’s requirements
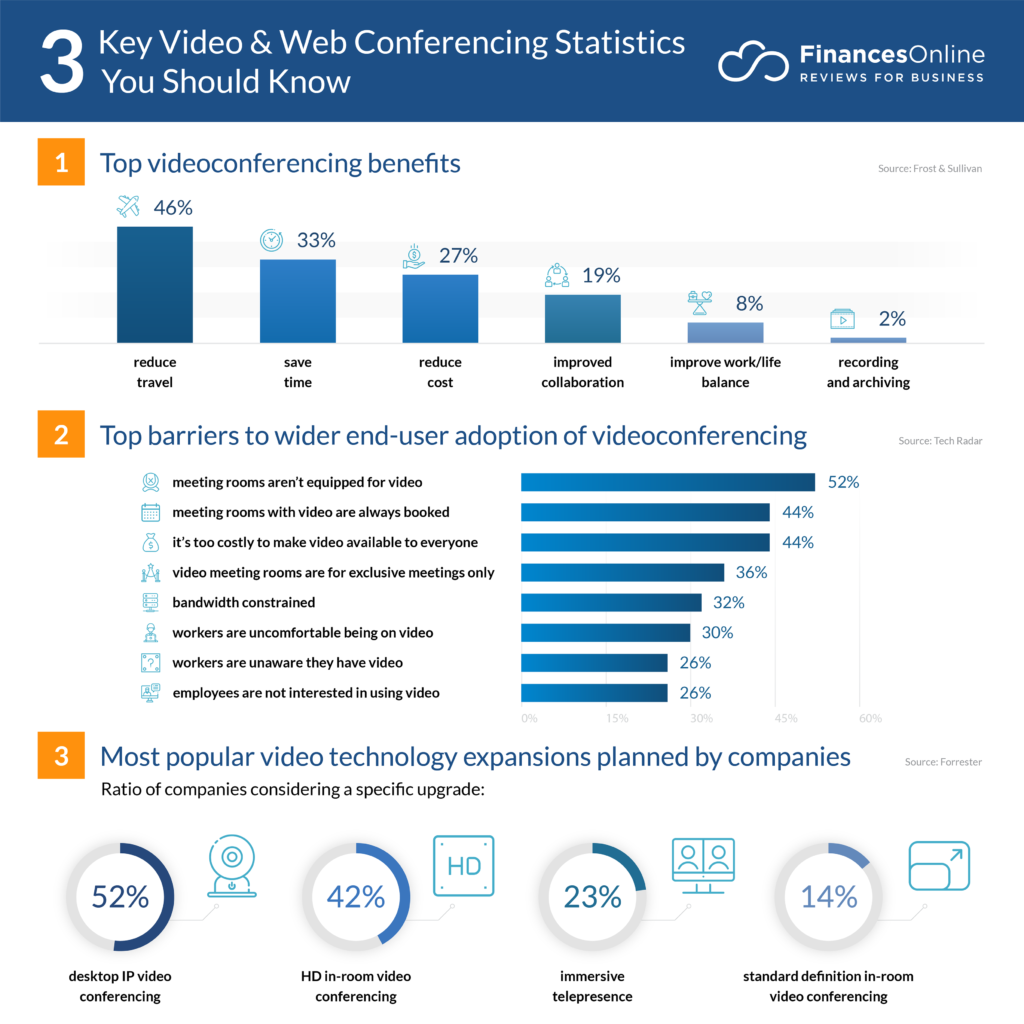
The application is supposed to contain features we can find in common video conferencing applications, such as audio and video calls, including screen sharing, instant messaging, file sharing, recording of the call, high-quality video, custom layouts, changing video background and end-to-end encryption. Additionally, the client requested call-control features too, such as waiting rooms, muting and kicking users, and raising a hand.
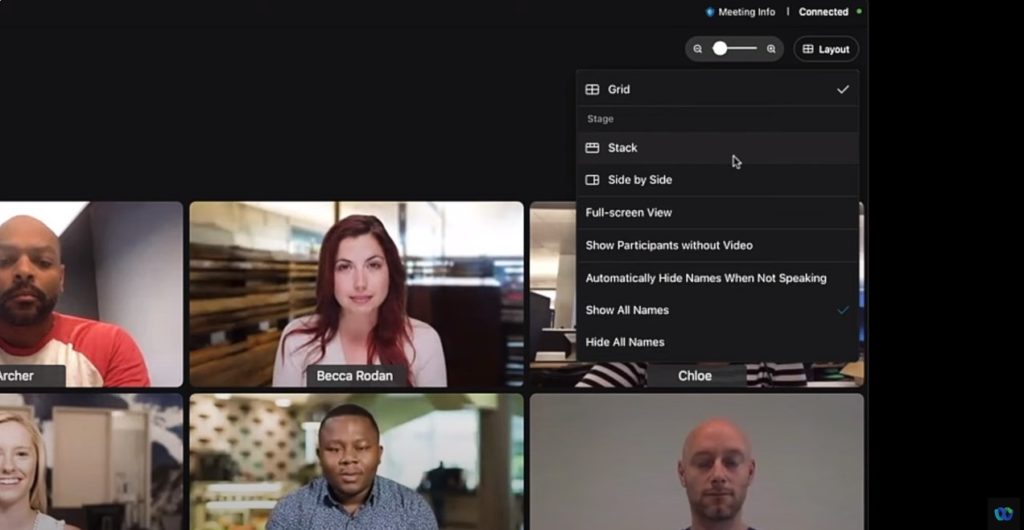
Discover the Layouts in Cisco Webex:
Technological challenges
Choosing the right technology is an important design decision during video conferencing application development because it impacts the performance and usability of the app, especially because the application processes live data from the users, and therefore, it has high requirements on architecture. For example, the WebRTC server has to support 100 participants in a video conference.
Traffic limits and costs
Continuing with the example, given that we have 100 participants in a call who stream HD-quality video which is 250 KBps and one client can see 10 video streams simultaneously on their screen, the client should have download traffic of 2.5 MBps and upload 0.25 MBps and the server should be able to handle to download 25 MBps and upload 250 MBps (per 100 users). As a result, we need to take into account the data transfer charges of our server provider when designing such a solution.
Data stream compatibility and transcoding
In order to save traffic, it is possible to resize the stream by either lowering the quality or lowering the resolution. We can achieve it by transcoding.
What is transcoding? Transcoding is a process of decoding, reformatting, and re-encoding video in order to decrease the size of a video stream or to make formats compatible with each other to be able to preview them on a device (which does not support the format).
Transcoding can help us also to bridge different formats used by Cisco SIP devices using Cisco SIP protocol. However, transcoding requires a GPU which costs more, monthly costs can be higher about $1 000 US dollars per server or more depending on GPU.
Regarding technology, we have good experience with GStreamer and FFMPEG technology to develop a transcoding layer for our applications.
However, there is a big question about the feasibility of transcoding which we need to ask. Is transcoding even worth implementing if it adds support for some additional devices?
Hardware requirements
Compatibility and signaling
SIP is a signaling protocol used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating communication sessions that include voice, video and messaging applications. SIP is used in Internet telephony, in private IP telephone systems, as well as mobile phone calling over LTE (VoLTE).
WebRTC is another protocol (or standard) next to SIP, which needs to be integrated with each other to be able to make calls from WebRTC to SIP and vice versa. The translation matrix of signaling messages from SIP to WebRTC needs to be designed and implemented using which SIP and WebRTC servers can communicate.
Security and end-to-end encryption
Some SIP servers do not implement security measures and cannot be facing the Internet because they would be hacked. For example, one of the most known PBX Asterisk.
What is PBX? PBX is a system that connects telephone extensions to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and provides internal communication for a business. An IP PBX is a PBX system with IP connectivity and may provide additional audio, video, or instant messaging communication utilizing the TCP/IP protocol stack.
End-to-end encryption is a very tricky case because clients (i.e. phones or end devices) need to communicate with each other to set up end-to-end encryption between each other and exchange their keys. We were facing the question: “Is it possible to establish an end-to-end encryption between a Cisco device and WebRTC client and even multiple participants?”
Want to get more tech insights?
PBX dockerization
Conveniently, we can package all our software using Docker. However, such containerization of software is tricky if we package specifically PBX software, because we need to explicitly define which ports will be exposed in the Docker configuration; enabling PBX to communicate with the phones using the exposed ports.
Our solution
Our solution is based on a couple of open-source existing products which we describe below, these products cover both client-side and server-side and their integration.
Client side
The client side is a client application that can be in your Android or iOS phone or simply in a web browser – or even a SIP phone, using which, you are able to join a video conference or perform an audio call.
Our preferred choice for the client application is Jitsi. It has a low-level JavaScript API for providing a customized UI for Jitsi Meet.
Jitsi is a collection of free and open-source multiplatform voice, video conferencing, and instant messaging applications for the web platform, Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, and Android.
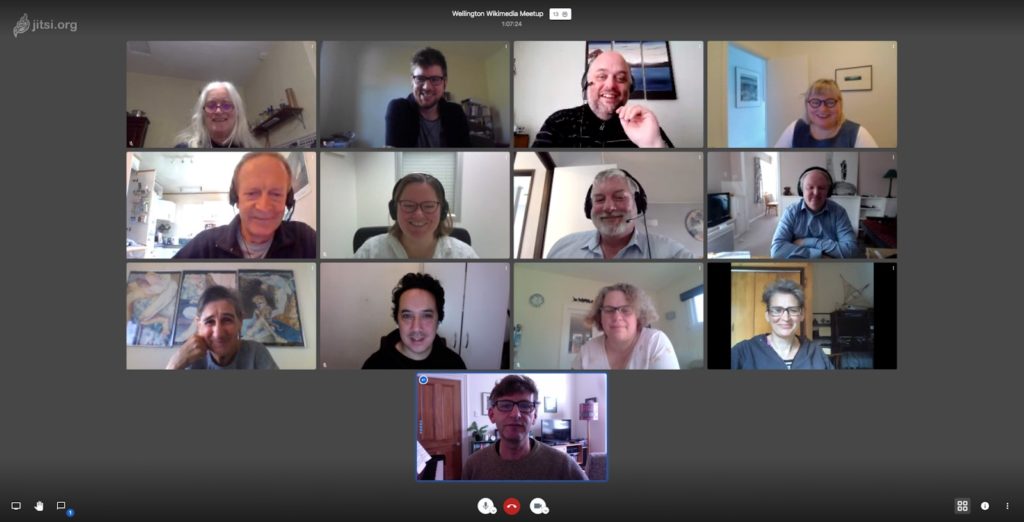
Jitsi actually includes much more than just a client. It is also a WebRTC and SIP server and SFU unit for multiparty conferences.
WebRTC server
You can choose from a couple of options. In the table below, you can see the most common WebRTC servers.
Mode | Web UI | Mobile APP | JS Library | Mobile SDK | Serverside Recording | Horizontal Scalability (out of the box) | |
Jitsi | SFU | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
Janus | SFU | x | x | yes | yes | yes | x |
Kurento | SFU/MCU | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | x |
Mediasoup | SFU | x | x | yes | x | yes | x |
Medooze | SFU/MCU | x | x | yes | yes | yes | x |
SIP server
Asterisk | SIP Foundry | Elastix | FreeSWITCH | PBXInAFlash | FreePBX | OpenSIPs | Kamailio | |
Free To Use | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Web-based GUI/Config | Yes | Yes | Yes | No (Third-party add-ons) | Yes | Yes | No | No (Third-party add-ons) |
Video Support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
IM/Chat | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Presence | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Auto Attendant/IVR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
Integration Support | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
Mobile Apps | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No |
WebRTC Support | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes |
Tip:
Did you know that you can build a SIP trunk between SIP servers and interface clients connected between multiple SIP servers – or even with devices having SIM cards resp. assign a SIM card to one of your SIP numbers?
Tip II:
To control cameras we can add another channel to SIP communication. Here is the example using Linphone, asterisk, and controlling with a camera with a keypad.
WebRTC end-to-end encryption
In the case of SIP-first PBX, the end-points (phones) have to support ZRTP which is a protocol based on which end-points can negotiate exchanging encryption keys and set up encrypted connections.
Please note that SRTP, even when deployed with SIP/TLS support, does not provide end-to-end encryption. The PBX is a trusted third party and can act as a man-in-the-middle to intercept traffic. Currently only ZRTP-enabled technology provides end-to-end encryption.
Conclusions
However, relying on the experienced software development partner, you will successfully overcome the possible challenges and get considerable benefits for your business at the best price-quality ratio. Altamira’s team, having deep expertise in the field will become the stable and reliable tech partner for making your business ambitions a reality.