Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR), represents the next stage in the digital transformation of the manufacturing indfustry. This evolution is fuelled by groundbreaking developments such as increased data usage and connectivity, advanced analytics, enhanced human-machine collaboration, and significant advancements in robotics.
We are currently experiencing a major shift in how we manufacture products, driven by the digitalisation of the industry. The journey began with the first industrial revolution, marked using water and steam power for mechanisation, followed by the second industrial revolution, which introduced mass production and assembly lines powered by electricity. The fourth industrial revolution builds on the third, which brought computers and automation, by advancing these technologies with smart and autonomous systems powered by data and machine learning.
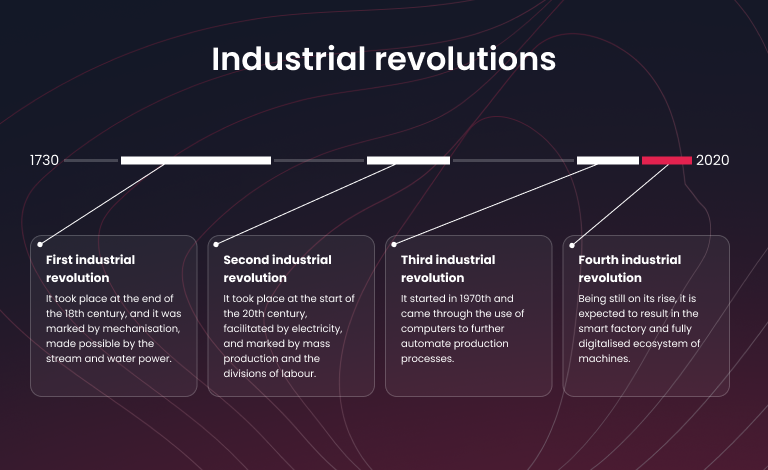
What is the Fourth industrial revolution?
Before 2014, the term “Industry 4.0” was rarely used, but by 2019, 68% of participants in a McKinsey global survey viewed it as a top strategic priority, with 70% reporting that their companies were already testing or implementing new technologies. Industry 4.0 builds on the advances of the Third Industrial Revolution, which spanned from the 1950s to the early 2000s and introduced computers, electronics, and the Internet. It pushes these innovations further with four key disruptive technologies applicable throughout the value chain:
- Connectivity, data, and computational power: Cloud technology, the Internet, blockchain, sensors.
- Analytics and intelligence: Advanced analytics, machine learning, artificial intelligence.
- Human-machine interaction: Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), robotics and automation, autonomous guided vehicles.
- Advanced engineering: Additive manufacturing (like 3D printing), renewable energy, nanoparticles.
What are the top technologies that are driving industrialization 4.0
Industry 4.0 is based on nine key technological pillars. These advancements connect the physical and digital ecosystems , enabling the creation of intelligent and autonomous systems. While many businesses and supply chains are already incorporating some of these cutting-edge technologies, the true power of Industry 4.0 is realised when they are integrated and used in unison.
Big Data and AI analytics
In the context of Industry 4.0, Big Data is gathered from a diverse array of sources, including assets, machinery, and IoT-enabled devices. This data collection goes beyond the factory floor, encompassing other parts of the business and external environments.
It can involve anything from customer feedback and market trends, which influence research, development, and design, to weather and traffic apps that optimise logistics. AI and machine learning-driven analytics are applied to this data in real-time, with the resulting insights enhancing decision-making and automation throughout smart manufacturing and supply chain management.
Discover expert insights on recent AI trends, use cases, and how you can stay ahead of this new age.
Horizontal and vertical integration
A crucial aspect of Industry 4.0 is the integration of processes both horizontally and vertically. Horizontal integration connects operational and business processes at the “field level,” ensuring inch-perfect coordination on the production floor, across various manufacturing sites, and throughout the entire supply chain.
Vertical integration, on the other hand, links all levels of an organisation, allowing data to flow smoothly. This means that production process is closely connected with business functions such as R&D, quality assurance, sales, marketing, and other departments, effectively breaking down data and knowledge silos and optimising overall operations.
Cloud computing
Often referred to as the “great enabler” of Industry 4.0 and digital transformation, cloud computing serves as the backbone for many advanced technologies. Modern cloud infrastructure supports innovations ranging from AI and machine learning to IoT integration, empowering businesses to drive progress.
Augmented reality
Augmented reality usually involves layering digital information onto the physical world. With an AR system, workers can use smart glasses or mobile devices to view real-time IoT data, digital components, repair or assembly guides, training materials, and more—all while focusing on a physical object such as equipment or a product. Although AR is still developing, it holds significant potential for predictive maintenance, service, quality assurance, technician training, and safety enhancements.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT), particularly its industrial application known as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), is so integral to Industry 4.0 that the terms are often used interchangeably. In Industry 4.0, most physical objects—such as devices, robots, machinery, equipment, and products—are equipped with sensors and RFID tags to deliver real-time data on their status, performance, or location. This technology enables companies to optimise supply chain, quickly design and adjust products, prevent equipment failures, monitor consumer preferences, track products and inventory, and much more.
Learn what are IoT Trends in manufacturing and what to expect in 2024.
Additive manufacturing/3D printing
Originally developed as a rapid prototyping tool, additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has expanded to serve a wide variety of purposes, from mass customisation to distributed manufacturing. With 3D printing, parts and products can be stored as digital design files in virtual inventories and produced on demand at the location where they are needed, minimising costs and reducing reliance on off-site or overseas manufacturing. The scope of 3D printing continues to expand each year, incorporating a growing array of materials such as metals, high-performance polymers, ceramics, and even biomaterials.
Autonomous robots
Industry 4.0 is ushering in a new era of autonomous robots designed to carry out tasks with minimal human input. These robots come in various sizes and functionalities, ranging from inventory scanning drones to autonomous mobile robots for picking and placing items. Featuring advanced software, AI, sensors, and machine vision, these robots can handle complex and precise tasks, as well as perceive, interpret, and respond to information from their environment.
Simulation/digital twins
A digital twin is a virtual representation of a real-world machine, product, process, or system, created using data from IoT sensors. As a fundamental element of Industry 4.0, digital twins enable businesses to gain deeper insights into, analyse, and enhance the performance and maintenance of their industrial systems and products. For example, an asset operator can use a digital twin to pinpoint a malfunctioning component, foresee potential problems, and optimise operational uptime.
Cybersecurity
As Industry 4.0 brings greater connectivity and extensive use of Big Data, robust cybersecurity becomes crucial. Employing a Zero Trust framework alongside technologies such as machine learning and blockchain allows organisations to automate the detection, prevention, and response to threats. This approach helps reduce the risk of data breaches and production interruptions throughout their networks.
What are the benefits of Industry 4.0?
Jeff Immelt, Former CEO of General Electric said: “To succeed in Industry 4.0, businesses must integrate smart technologies and create a culture that embraces digital transformation and continuous learning.” Indeed, Industry 4.0 requires organizations to implement systematic training at all organizational levels and it has been driven by changes relating to technological capabilities and processes. It offers various advantages to organisations that adopt it.
Enhanced process visibility
Industry 4.0 technologies enable original equipment manufacturers to track actual product usage by customers compared to its intended use.
Improved machinery monitoring
With real-time sensor data, organisations can oversee manufacturing processes more effectively. This data can be analysed against a digital twin—a model operating at ideal efficiency—to identify areas for process improvement.
Advanced training methods
Some organisations take advantage of Industry 4.0 principles for employee training, employing augmented reality to instruct workers on machinery operation and safety procedures before they step onto the factory floor. This type of training is also applied in areas like fire suppression and first aid.
Minimising downtime
Before Industry 4.0, industrial machinery was serviced according to manufacturer schedules. With Industry 4.0 technology, machinery fitted with sensors can continuously monitor its own health. This allows organisations to predict potential issues before they arise and take proactive measures to address them. In some instances, machines can even automatically reorder replacement parts when necessary. This capability helps prevent costly production stoppages and reduces downtime.
Boosted productivity
Digital technologies integrated on the factory floor connect with corporate data systems, facilitating big data analytics of manufacturing-related data. Advanced analytics help organisations identify trends and gain valuable insights, leading to increased productivity and profitability.
Cost reduction
Industry 4.0 technologies can identify and mitigate issues such as equipment malfunctions and excessive resource consumption, which can help lower costs.
When effectively implemented, Industry 4.0 solutions offer compelling benefits. In various industries, it is typical to observe reductions in machine downtime by 30 to 50 percent, increases in throughput ranging from 10 to 30 percent, enhancements in labour productivity by 15 to 30 percent, and forecasting accuracy improvements of up to 85 percent.
What are the Industry 4.0 applications today?
Although some organisations may still be skeptical about the potential effects of Industry 4.0 on their business or are facing challenges in acquiring the necessary talent or expertise for effective implementation, many others are already making changes and gearing up for a future where intelligent machines enhance their operations. Here are just a few of the possible applications.
Identify opportunities
Optimise logistics and supply chains
A networked supply chain can adapt to new information as it arises. For example, if a shipment is delayed due to weather, a connected system can proactively respond by adjusting manufacturing priorities accordingly.
Autonomous equipment and vehicles
Some shipping yards are utilising autonomous cranes and trucks to enhance efficiency as they unload shipping containers from vessels.
Robots
Previously reserved for large companies with substantial budgets, robotics have become more cost-effective and accessible to organisations of all sizes. Autonomous robots can now assist manufacturers with tasks ranging from picking products in a warehouse to preparing them for shipment.
For example, Amazon uses robots to transport goods within its warehouses, which helps cut costs and optimise floor space for the online retailer.
Although Industry 4.0 is still developing and its full impact may only be clear in hindsight decades from now, companies embracing these technologies are already reaping rewards.
What are the requirements of Industry 4.0?
The Fourth Industrial Revolution focuses on data, communication, and connectivity. Industry 4.0 aims to automate manufacturing processes using cyber-physical systems that gather, analyse, and transmit data across interconnected networks.
Let’s explore essential requirements for obtaining the automated data intelligence necessary to realise Industry 4.0.
Smart communication
Communication has evolved dramatically over the past 200 years. In the United States, systems like The Pony Express revolutionised mail delivery by using a network of horses to transport letters swiftly across the country, a significant improvement over the slower wagon trains that took weeks or months.
The advent of the telegraph was transformative, enabling instant communication across vast distances. Around the same period, locomotives began transporting large volumes of information and documents by rail.
The invention of the telephone allowed for real-time conversations over long distances, followed by the development of computer intranets. This progression culminated in the expansion of connected intranets into the World Wide Web and the modern Internet.
Since the 1990s, the speed of data communication has surged exponentially. So, now it’s a must to establish a well-thought engagement strategy to enable consistent communication with critical senior stakeholders, leaders, and a cross-functional core team.
Industry 4.0 represents a revolution in communication and interconnectivity. Emerging technologies are now enabling advanced smart communication. Rather than relying on humans to interpret and analyse data with some machine assistance, smart devices are taking on the role of communicating with minimal human intervention.
The sheer volume of data now exceeds human capacity for analysis and decision-making. Coupled with advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence, this data overload allows machines to accelerate manufacturing processes by handling data at unprecedented speeds and scales.
Moreover, machines and systems are starting to overcome previous human bottlenecks by autonomously communicating and making decisions without human input. The point of Industry 4.0 is to achieve intelligent communication where machines interact with other devices, driving factory automation.
Data quality
Data is fundamental to Industry 4.0, with factory automation relying heavily on the gathering and transmission of data. Yet, the efficiency of data intelligence and communication hinges on the quality of the data itself. If any part of the data is incomplete, the entire system risks failure.
Traditionally, the emphasis has been on amassing as much data as possible rather than collecting data that is useful and compatible across systems. For Industry 4.0 to be realised, the next decade must prioritise actionable insights and machine-driven automated decision-making. In essence, data quality outweighs data quantity. Excessive amounts of low-quality data lead to higher resource consumption and less accurate results.
To take benefit of Industry 4.0, companies need to manage data flow both within their organisation and with external partners, establishing a continuous digital thread of information across all departments.
Additionally, maintaining data accuracy in areas that generate new data, such as engineering, procurement, and manufacturing, is inevitable. If any segment of data is missing, it disrupts the digital thread and halts data flow.
Smart devices
An illustration of Industry 4.0’s connected smart devices is visual sensors mounted on robotic arms that exchange data. This also encompasses equipment such as autonomous robots that transport products across the factory floor and handle heavy materials precisely when needed.
Industrial smart devices use sensors to gather data for making autonomous decisions while continuously interacting with a broader network. This automated communication allows for seamless synchronisation throughout smart factories.
Digital transformation
The digital transformation involves strategically shifting from traditional analogue methods or outdated digital processes to a more automated systems approach.
Digital transformation is usually a comprehensive initiative aimed at reducing costs and boosting profit margins through digital advancements. In this context, Industry 4.0 plays a crucial role in the digital transformation of a company’s engineering, procurement, and manufacturing departments.
The final words
Industry 4.0 represents a transformative shift in how businesses operate, offering never-seen opportunities for efficiency, innovation, and business growth. By embracing the technologies and strategies defined by this industrial era—such as IoT, AI, big data, embracing automation—companies can yield significant value, streamline their operations, and gain a competitive edge.
However, capturing benefits of Industry 4.0 requires a clear understanding of its principles, a commitment to digital transformation, and a strategic approach to integrating these advanced systems into every facet of the business.
Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft reiterated that “Industry 4.0 is not just about technology but also about innovation and a new way of thinking about how we create value and deliver it to our customers.”
How Altamira can help?
From cutting-edge manufacturing software to advanced analytics, Altamira’s Industry 4.0 consulting services focus on enhancing your core competencies with emerging and relevant technologies to future-proof your business. Our goal is to make your processes more flexible through scalable and sustainable digital solutions.
Altamira’s Board member, Dmitry Kushnir, shared his insights about how Altamira contribute to and support Industry 4.0 concepts.
A big part of the 4th industrial revolution will be easy access to diverse data that can be used for analysis and achieving better intelligence. It can help your company continuously improve customer satisfaction, increase sales, and optimise costs.
Such data is now accessible in real-time in the form of text, speech, image, and video formats. At Altamira, we aim to enable customers to access such data in real-time and achieve superior analytical capabilities. With the latest developments in AI, our team keeps developing use cases and implementing them for our clients.
One example is inspecting damaged objects, such as durable goods, cars, property, etc., utilising the latest capabilities of image recognition. This makes the inspection of such damaged goods quick and efficient. What's more important is that you can scale such inspections with very attractive marginal costs while continuously improving the quality of the outcomes.
Altamira also works with partners that develop new AI-enabled solutions. With the AI product from Ender Turing company, we aim to help insurance companies, banks, and healthcare providers achieve real-time access to conversational analytics at customer centers / call centers and continuously improve the quality of service provided.
A big part of Altamira's service portfolio is software solutions development. To help our customers be quicker to market with their solutions, Altamira team uses AI tools and proprietary frameworks to compress the software development lifecycle.
At every project’s discovery stage, we consider options for how we can build customer solutions much faster, with lower expenses, while keeping the quality of outcomes at a high level. With the evolution of AI and open-source tools, we constantly work to improve our methodologies and approaches that can bring extra benefits to our clients.Dmitry Kushnir, Board member
We analyse the impacts of these technologies in relation to your business and identify new opportunities to boost productivity and accelerate time to revenue. Contact us to get a free expert consultation!

